Today’s Russia realizes that it has been unable to swallow Ukraine in one gulp. Making a virtue out of necessity, it has therefore decided to apply the salami tactic to Ukraine: slice by slice…
The announcement of the Russian-Ukrainian negotiations has raised hopes in the West, and stock markets have rebounded. Is this enthusiasm justified? Is a compromise possible?
By Françoise Thom – DeskRussia – April 2, 2022 —
A careful reading of the statements of the Russian leaders and their representatives should be enough to dampen the hopes of the optimists.
The current round of talks between Russia and Ukraine does not mean a change in Moscow’s plans, said Russian presidential spokesman Dmitry Peskov. De-escalation in the directions of Kiev and Chernihiv does not mean a complete ceasefire, said the head of the Russian delegation, presidential aide Vladimir Medinsky, in talks with Kiev.
Statement by Vladimir R. Medinsky after the talks – Photo © E-S
All this is punctuated by the relentless bombing of Ukraine. And the fierce intransigence of President Putin is well known. The question then arises, what are Russia’s aims through these negotiations that dangle in front of Ukraine and the West?
As often the case, it is enlightening to refer to the Soviet past because current leaders of the Kremlin have a similar conception of “compromise” as earlier Bolshevik leaders. Above all, we must start from an analysis of the “correlation of forces”.
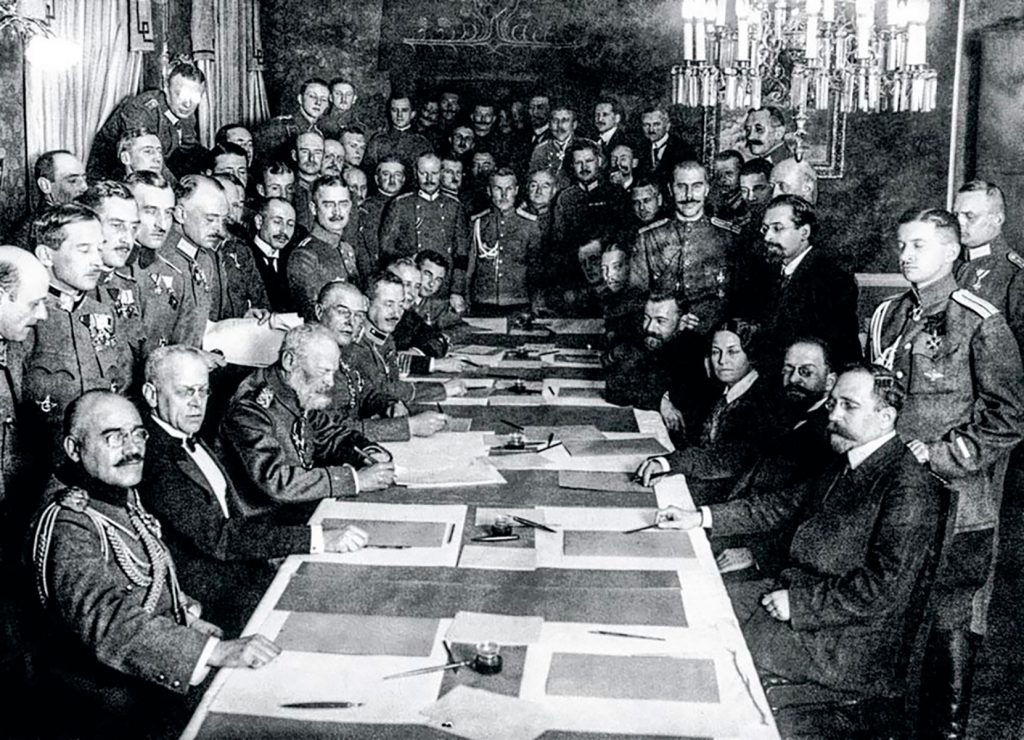

Engaged on the side of the Allies from the beginning of the First World War, the Russian army suffered serious setbacks, particularly in East Prussia, where it was crushed at Tannenberg in August 1914. Then the situation will get worse in 1915. The « supposedly short » war was beginning to have an effect throughout the Russian Empire. The cause, in particular, was « supply difficulties and poor logistics combined with the negligence of military leaders who had encouraged massive desertions ».[1]
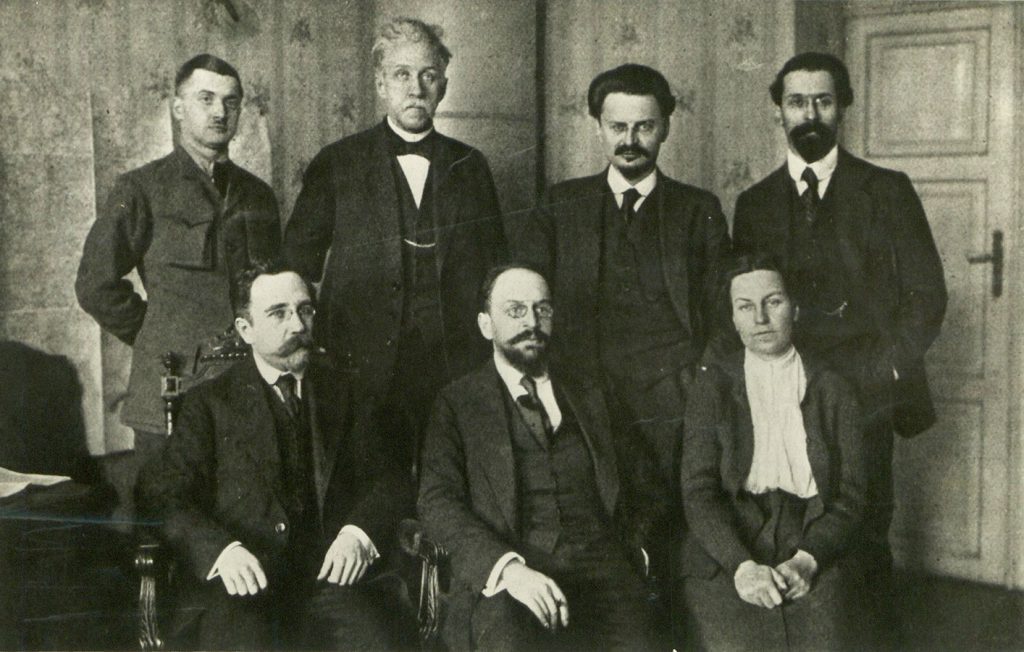

On 15 December 1917, an armistice was concluded between Soviet Russia and the Central Powers. Talks continued in search of a peace treaty, despite the opposition of the Russian delegation, Trotsky and influential members of the Central Committee who favoured a revolutionary war. Lenin had no choice but to accept the « shameful peace treaty » which took away from Russia Finland, Poland, the Baltic States, Ukraine and a part of Belarus, depriving Russia of 90% of its coal production, 70% of its metallurgy and 55% of its agricultural wealth, in particular Ukrainian wheat. EDITOR’S NOTE
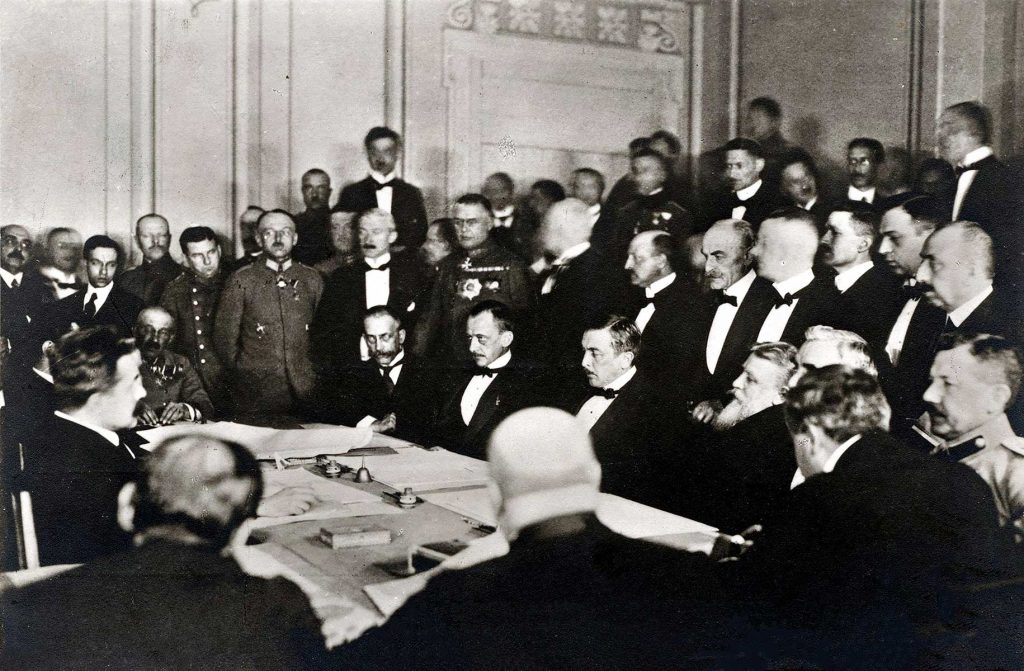

Let’s listen to Lenin’s arguments defending the Brest-Litovsk agreements in March 1918: “Now that we have signed the peace, we have a respite, we will use it to defend the fatherland better than by war, because if we had a war, we would have this army in panic and a stampede that we would have to stop and that our comrades cannot stop, because it is impossible, the war being stronger than preachings, than ten thousand reasons […] Peace is a way to gain strength. […] Take advantage of the respite that has been granted, even if only for an hour, to maintain contact behind the lines and to create new armies there.”
We know how much Putin and his circle admire the German-Soviet pact: the compromise with Berlin made it possible for the USSR to swallow up the Baltic States and the eastern provinces of Poland. The agreement with Hitler radically altered the “correlation of forces” in Europe to Moscow’s advantage.
Today’s Russia realizes that it has been unable to swallow Ukraine in one gulp, as it had believed in the early hours of the offensive. Making a virtue out of necessity, it has therefore decided since March 25th to apply the salami tactic to Ukraine: slice by slice. The priority now is the annexation of the Donbass within its administrative borders (the separatist entities represent only a third of the region’s territory), which Sergei Rudsky, the head of the main operational directorate of the General Staff of the Russian Armed Forces, calls “the total liberation of the Donbass”.

The separatist leaders are already discussing a referendum to merge their entities into Russia. This does not mean that Putin has given up his initial objectives, the control over all of Ukraine. But in the meantime negotiations are used to sow confusion and uncertainty in the camp of the adversary, to put Zelenski (and Westerners) in front of the tragic choice between continuing the war and the further amputation of a third of the Ukrainian territory, to reap the concessions already extracted from Kiev, neutrality, the possibility of delaying the status of Crimea, before formulating new claims. However, Peskov has already rejected the Ukrainian proposal for a 15-year consultation period on the status of Crimea. “We will not invade Crimea, it is part of Russia,” he said. “Our constitution forbids us to discuss the fate of Russian territories or the fate of Russian regions with anyone, it is excluded.” One remembers the old principle of negotiations with Moscow that is summed up by a joke at the time of the Cold War: “What is ours is ours, what is yours is negotiable”.

The Istanbul negotiations created a storm of indignation among the ultra-patriots on Russian television. It is significant that they were compared to those of Khasaviourt. On August 31, 1996, the Khasavyurt agreements ended the first Chechen war. After the failure of Russian forces to retake the capital Grozny, General Alexander Lebed and Aslan Maskhadov, the future president of Chechnya, agreed to stop hostilities, withdraw federal troops, and to postpone the main issue, the status of the republic, until the end of 2001.
Françoise Thom – Portrait © E-S
The Istanbul negotiations created a storm of indignation among the ultra-patriots on Russian television. It is significant that they were compared to those of Khasaviourt. On August 31, 1996, the Khasavyurt agreements ended the first Chechen war. After the failure of Russian forces to retake the capital Grozny, General Alexander Lebed and Aslan Maskhadov, the future president of Chechnya, agreed to stop hostilities, withdraw federal troops, and to postpone the main issue, the status of the republic, until the end of 2001. At the time, this agreement was fiercely attacked by the “red-browns” as a shameful capitulation. But according to Alexander Barkhatov, spokesman for Alexander Lebed, who was present at the talks, “the Khasavyurt agreement was signed not to conclude peace at the cost of a promise to consider the question of the sovereignty of Ichkeria [Chechnya]. The purpose of the agreement from the beginning was really to gain time to carry out a regrouping of forces, including the creation of several shock detachments.” And also not to be forgotten, President Aslan Maskhadov, the Chechen signatory to these agreements, was assassinated by the FSB in 2005.
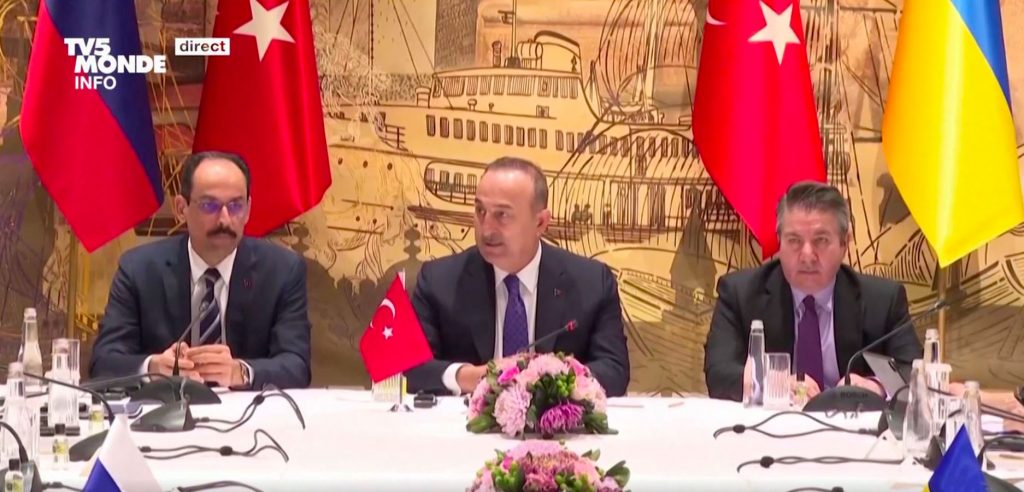

Russia’s so-called negotiations are really window-dressing for other reasons as well. The very official Regnum agency believes that “for tactical and strategic reasons, it is not advantageous for Moscow to consider the mission of the Ankara mediation in the Ukrainian crisis a failure.” Moscow hopes to weaken the West’s solidarity, whose wavering the Kremlin watches with pleasure, encouraged by the obstinacy of President Macron to maintain his masochistic dialogue with Putin. Everything that encourages European countries to go it alone is being implemented by Moscow.

Already, voices are being raised in the West to plead for a relaxation of sanctions in order to encourage Russia to engage in “dialogue”, confirming the Kremlin’s Kremlin’s certainty that sanctions will be short-lived, that the hardening of Western policies will not last. Putin has by no means given up on having his cake [the gobbling up of Ukraine] and eating it too [Western technology transfers and funding; eventually, domination of the European continent]. To quote Vzgliad again: “Russia expects that the military-political success will lead to the return of normal relations [with the West]. And, in the first place, to the lifting or easing of what the West calls ‘sanctions’”. Again, the evolution of the correlation of forces looks promising from Moscow’s perspective. The Kremlin is certain to have the Russian population well in hand whatever happens, even if the Russians are reduced to a survival economy. While in the West the disruption of energy supplies from Russia and the the subsequent increase in the price of food, fuel and basic necessities will create a tidal wave of discontent that Moscow hopes will benefit the populist leaders close to the Kremlin. All this “will lead to the definitive break-up of the collective West, and especially the European Union, into national ‘principalities’.”

We have underestimated the evil of Putin’s Russia for 20 years.[2]
The reactions to the announcement of the Istanbul talks show that we continue to do so.
Putin is ready to push Russia into the abyss, provided he can realize his idée fixe, the destruction of Europe and the Western world. He is bombing the fuel supplies in Ukraine at the time of sowing of the fields, to add the spectre of famine to all the scourges he has already unleashed on mankind.
Image PX © Irik Jarov
We have underestimated the evil of Putin’s Russia for 20 years. The reactions to the announcement of the Istanbul talks show that we continue to do so. Putin is ready to push Russia into the abyss, provided he can realize his idée fixe, the destruction of Europe and the Western world. He is bombing the fuel supplies in Ukraine at the time of sowing of the fields, to add the spectre of famine to all the scourges he has already unleashed on mankind.
Putin has staked everything on the aggression against Ukraine. He will not let go of his prey. The sooner we understand this, the better we will be able to face a danger that our wait-and-see attitude and our futile hopes will not make disappear.[3]
[1] The Treaty of Brest-Litovsk between the Central Empires and Ukraine, also known as the Brest-Litovsk Peace Treaty of 9 February 1918, was negotiated between diplomats of the Central Empires and representatives of the young Ukrainian People’s Republic. This peace treaty put an end to the war between Ukraine, then engaged in a process leading to independence, and the Central Empires. Concluded without the knowledge of the Russian negotiators, the treaty resulted in the recognition of Ukraine’s independence. However, military developments on the Western Front and the rapid collapse of the Ukrainian People’s Republic forced Germany and Austria-Hungary, the main parties interested in peace with Ukraine, to intervene militarily in the country. A peace of victory, this treaty was rendered null and void by the Rethondes armistice, forcing the Reich to denounce all the treaties signed during 1918. (Sources: Wikipedia and History for All).
[2] See « Comprendre le poutinisme – Pour sortir du mensonge » by Françoise Thom, published by Desclée de Brouwer (February 2018).
This well-documented book, written by a historian specialising in post-communist Russia, finely deciphers the « neo-totalitarian » drift of a power born in the bloody crucible of the war in Chechnya, cultivating nationalism and « paranoia » to excess, preferring to sacrifice public freedoms on the altar of a Great Russia erected as the guardian of traditions and religious orthodoxy. According to the author, this post-Soviet Russia is structured, as in the time of the tsars, by a vast territorial « empire » controlled by a centralising and prevaricating power, which arbitrarily and systematically confiscates, to the detriment of the general interest, the wealth of this vast country, to the benefit of an oligarchy subservient to a « clan » and its leader, Vladimir Putin. In the end, Françoise Thom deciphers the objectives of current Russian international policy, which, under the guise of promoting the « Russian world » and a « Eurasian economic union » led from Moscow, has engaged in a « duel » to the death against the European Union and Western democracies. This book sounds a cry of alarm in the face of Vladimir Putin’s interference and « desire » to « spread chaos » outside his borders, on the one hand by supporting the « most odious dictatorships », as in Syria, and on the other hand, by supporting, including financially, the most reactionary political movements in Europe and the United States. (Source: Julien Jacob in Esprit).
[3] In Le Figaro, French Foreign Minister, Jean-Yves le Drian says: « Putin has woken up Ukraine, Europe and NATO… The Russian president’s goal is a « complete occupation » of the country whose « very existence » as a state he denies » … « Is the goal to recover territories that Vladimir Putin says belong to Russia or is it the full occupation of Ukraine and its integration into a rump state? Judging by the Russian president’s speeches, the second hypothesis prevails for the moment. In any case, this is the driving force behind Russian aggression. Does he have the means to implement it in the long term? That is the question that arises. (Le Figaro, Interview with Isabelle Lasserre – 01.04.2022
See also: « Pourparlers d’Istanbul : que veut la Russie ? » in DeskRussie (2022-04-01)
Françoise Thom’s publications on DeskRussia (2022)

- Pourquoi le système poutinien porte la guerre comme la nuée porte l’orage in DeskRussie (2022-06-17)
- Why the Putin System Carries war Like a Cloud Carries a Storm in DeskRussia (2022-06-17)
- La rhétorique de l’agresseur in DeskRussie (2022-06-03) Françoise Thom
- The Rhetoric of the Aggressor in DeskRussia (2022-06-03)
- L’autre offensive russe in DeskRussie (2022-05-20)
- The Other Russian Offensive in DeskRussia (2022-05-20)
- L’orthodoxie spéciale du pape François in DeskRussie (2022-05-20)
- The special orthodoxy of Pope Francis in DeskRussia (2022-05-20)
- L’ivresse de la transgression in DeskRussie (2022-05-06)
- Reveling in Transgression in DeskRussia (2022-05-06)
- Réflexions mélancoliques sur l’élection française in DeskRussie (2022-04-22)
- Melancholic reflections on the French elections in DeskRussia (2022-04-20)
- Les idéologues russes visent à liquider la nation ukrainienne in DeskRussie (2022-04-06)
- Russian Ideologues Aim to Liquidate the Ukrainian Nation in DeskRussia (2022-04-08)
- Pourparlers d’Istanbul : que veut la Russie ? in DeskRussie (2022-04-01)
- Istanbul Talks: What Does Russia Want? in DeskRussia (2022-04-02)
- Les leçons d’une fin de règne : Staline 1952-3, Poutine 2022 in DeskRussie (2022-03-25)
- The lessons of an end of reign: Stalin 1952-3, Putin 2022 in DeskRussia (2022-03-25)
- Poutine, ou l’histoire alternative contre l’histoire tout court in DeskRussie (2022-03-18)
- Alternative History Against History: the Case of Vladimir Putin in DeskRussia (2022-03-18)
- Le monde de l’après-guerre vu de Russie in DeskRussie (2022-03-11)
- The Post-war World Seen from Russia in DeskRussia (2022-03-12)
- Poutine ou la passion de la malfaisance in DeskRussie (2022-03-04)
- Putin or the Passion for Evil in DeskRussia (2022-03-02)
- La kremlinophilie française : un mal incurable ? in DeskRussie (2022-02-25)
- French Kremlinophilia: an Incurable Disease? in DeskRussia (2022-02-26)
- Le dressage de l’Europe : comment le Kremlin exploite la crise ukrainienne in DeskRussie (2022-02-11)
- How to Train Europe: the Kremlin’s Exploitation of the Ukrainian Crisis in DeskRussia(2022-02-11)
- Poutine : le flirt avec l’apocalypse in DeskRussie (2022-01-28)
- Putin: Flirting With Armageddon in DeskRussia (2022-01-28)